Prompt Engineering Guidelines
Prompt Engineering 1
Prompt Engineering Guidelines
In this tutorial, we’ll practice two prompting principles and their related tactics in order to write effective prompts for large language models.
What is prompt engineering?
The inputs to LLMs are referred to as “prompts”
Designing a prompt is essentially how you “program” a LLM:
- with instructions
- or some examples of how to successfully complete a task
Prompt engineering
- methods to improve model reasoning
- reduce the likelihood of model hallucinations
Prompting in ChatGPT
We use OpenAI’s API
The OpenAI API can be applied to virtually any task that requires understanding or generating natural language and code.
Can also be used to generate and edit images or convert speech into text.
Example prompt
- Example prompt with a system message (helps set the behavior of the assistant)
f: Formatted strings allow you to embed expressions inside string literals, using curly braces {}""": Triple double-quotes are used to denote a string that spans multiple lines.\: line breaks are used to make the text more readable{text}is a placeholder for a variable text that will be placed into the string at that position.
Example text
text = f"""
You should express what you want a model to do by \
providing instructions that are as clear and \
specific as you can possibly make them. \
This will guide the model towards the desired output, \
and reduce the chances of receiving irrelevant \
or incorrect responses. Don't confuse writing a \
clear prompt with writing a short prompt. \
In many cases, longer prompts provide more clarity \
and context for the model, which can lead to \
more detailed and relevant outputs.
"""Chat completion helper function
1def get_completion(prompt, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"):
2 messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
3 response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
4 model=model,
5 messages=messages,
6 temperature=0)
7 return response.choices[0].message["content"]- 1
-
Defines the function
get_completionwith two parameters - 2
-
Dictionary with two key-value pairs (role as
"user"; content asprompt) - 3
-
Initiates an API call to OpenAI’s ChatCompletion method; result is stored in a variable named
response. - 4
-
Specifies the model to be used (we always use
"gpt-3.5-turbo") - 5
-
Passes the
messageslist to the API - 6
- The degree of randomness of the model’s output (0 makes the model’s output more focused and deterministic).
- 7
- Extracts and returns the content of the message.
What is a sytem message?
The system message is optional and helps set the behavior of the assistant.
You can modify the personality of the assistant or provide specific instructions about how it should behave
- You can use specific personas (e.g. write in the style of Socrates)
- If outputs are too simple, ask for expert-level writing.
- If you dislike the format, demonstrate the format you’d like to see.
What is the temperature?
Lower values for temperature result in more consistent outputs
Higher values generate more diverse and creative results.
Select a temperature value based on the desired trade-off between coherence and creativity for your specific application.
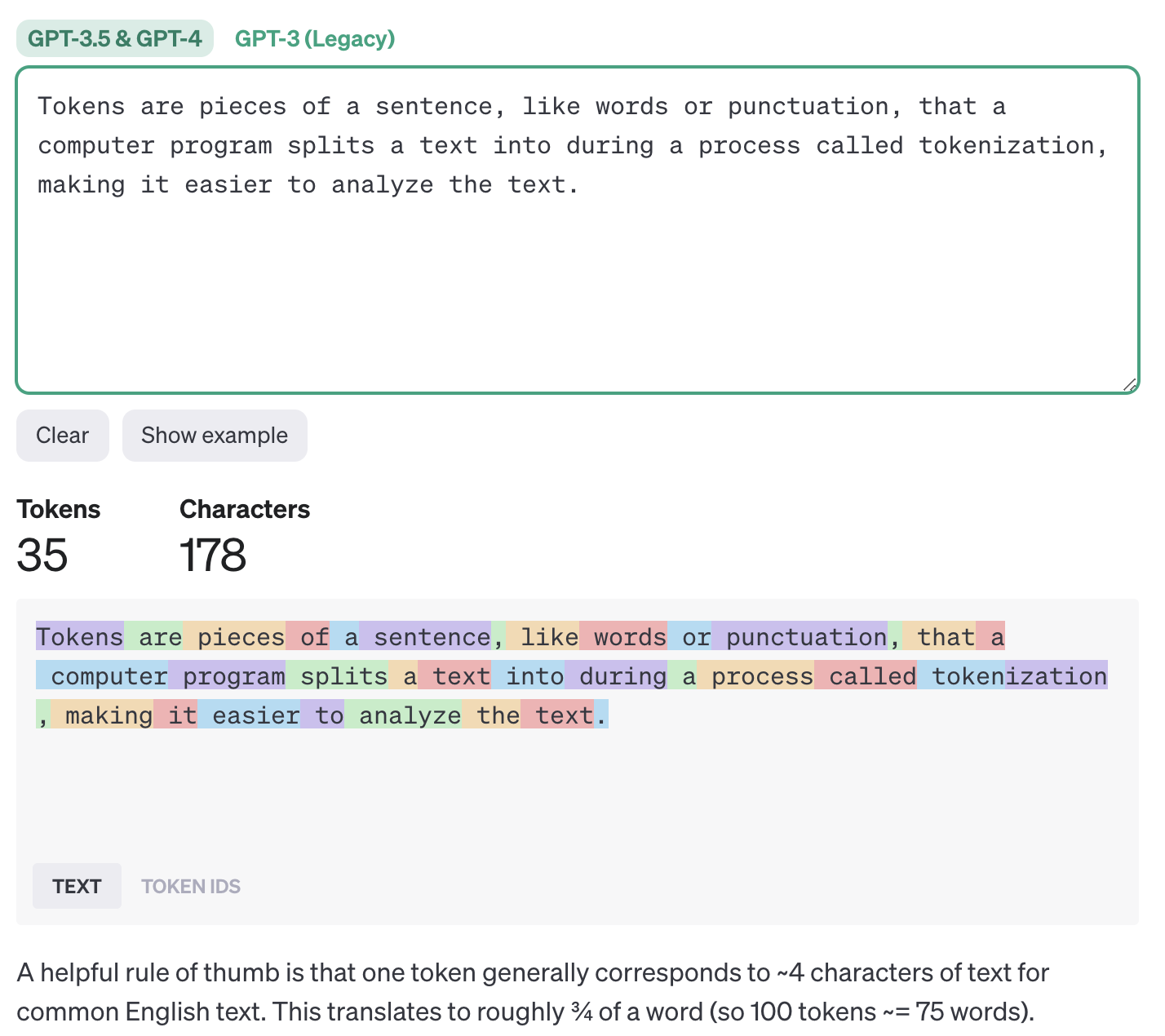
What are tokens?
Language models read and write text in chunks called tokens.
In English, a token can be as short as one character or as long as one word (e.g., a or apple),
For example, the string “ChatGPT is great!” is encoded into six tokens:
["Chat", "G", "PT", " is", " great", "!"].
Tokens
Tokens and API calls
- The total number of tokens in an API call affects:
- How much your API call costs, as you pay per token
- How long your API call takes, as writing more tokens takes more time
- Whether your API call works at all, as total tokens must be below the model’s maximum limit (4097 tokens for gpt-3.5-turbo)
Setup
API key and Python libaries
Helper function
Principle 1: Be clear and specific
Write clear and specific instructions
Use delimiters
- Always use delimiters (like backticks) to clearly indicate distinct parts of the input
text = f"""
You should express what you want a model to do by \
providing instructions that are as clear and \
specific as you can possibly make them. \
This will guide the model towards the desired output, \
and reduce the chances of receiving irrelevant \
or incorrect responses. Don't confuse writing a \
clear prompt with writing a short prompt. \
In many cases, longer prompts provide more clarity \
and context for the model, which can lead to \
more detailed and relevant outputs.
"""
prompt = f"""
Summarize the text delimited by triple backticks \
into a single sentence and add a joke or playful comment
```{text}```
"""
response = get_completion(prompt)
print(response)- Output: “To get the desired output from a model, it’s important to give clear and specific instructions, and remember that longer prompts can actually be more helpful in providing context and clarity—just like how a detailed joke is often funnier!”
Ask for structured output
- Ask for a structured output (e.g. JSON, HTML, …)
Output
{
"books": [
{
"book_id": 1,
"title": "The Enigma of Elysium",
"author": "Evelyn Sinclair",
"genre": "Mystery"
},
{
"book_id": 2,
"title": "Whispers in the Wind",
"author": "Nathaniel Blackwood",
"genre": "Fantasy"
},
{
"book_id": 3,
"title": "Echoes of the Past",
"author": "Amelia Hart",
"genre": "Romance"
}
]
}Check whether conditions are satisfied
text_1 = f"""
Begin with a clear understanding of the desired outcome from the prompt, including the \
kind of information and format you seek in the response. Familiarize yourself with the \
capabilities and limitations of the model you're working with, ensuring you know its \
strengths and weaknesses in generating text. Draft a preliminary version of your prompt, \
keeping it concise yet detailed enough to guide the model towards the desired outcome. \
Test the preliminary prompt with the model, analyzing the generated responses for \
accuracy, relevance, and completeness. Refine the prompt based on the feedback from the \
initial testing, adjusting the language, structure, or additional details as necessary. \
Perform multiple rounds of testing and refinement, continually honing the prompt for \
better results. Document the final version of the prompt and any notable observations from \
the testing process for future reference and learning.
"""prompt = f"""
You will be provided with text delimited by triple backticks.
If it contains a sequence of instructions, \
re-write those instructions in the following format:
Step 1 - ...
Step 2 - …
…
Step N - …
If the text does not contain a sequence of instructions, \
then simply write \"No steps provided.\"
```{text_1}```
"""Response
Completion for Text 1:
Step 1 - Begin with a clear understanding of the desired outcome from the prompt, including the kind of information and format you seek in the response.
Step 2 - Familiarize yourself with the capabilities and limitations of the model you're working with, ensuring you know its strengths and weaknesses in generating text.
Step 3 - Draft a preliminary version of your prompt, keeping it concise yet detailed enough to guide the model towards the desired outcome.
Step 4 - Test the preliminary prompt with the model, analyzing the generated responses for accuracy, relevance, and completeness.
Step 5 - Refine the prompt based on the feedback from the initial testing, adjusting the language, structure, or additional details as necessary.
Step 6 - Perform multiple rounds of testing and refinement, continually honing the prompt for better results.
Step 7 - Document the final version of the prompt and any notable observations from the testing process for future reference and learning.Use “few-shot” prompting with examples
- In few-shot prompting, examples are included directly in the prompt.
- These examples serve as a reference or guide for the model to understand the task at hand.
- Few-shot prompting can be an effective technique in prompt engineering, helping to guide the model’s responses without the need for additional training data or fine-tuning.
Few-shot example
prompt = f"""
Your task is to answer in a consistent style.
<child>: Teach me about patience.
<grandparent>: The river that carves the deepest \
valley flows from a modest spring; the \
grandest symphony originates from a single note; \
the most intricate tapestry begins with a solitary thread.
<child>: Teach me about resilience.
"""- Output: <grandparent>: Resilience is the unwavering strength that emerges from facing adversity. It is the ability to bounce back, to rise above challenges, and to persevere in the face of obstacles. Just like a tree that bends but does not break in a storm, resilience allows us to weather the storms of life and come out stronger on the other side.
Principle 2: Time to think
Give the model time to “think”
Specify the the steps and output
text = f"""
Prompt engineering is a pivotal aspect of harnessing the full \
potential of language models such as OpenAI's ChatGPT. It serves \
as a conduit between human intent and machine comprehension, \
facilitating a clearer transmission of the task or information desired. \
By meticulously crafting prompts, individuals can steer ChatGPT towards \
delivering more precise, pertinent, and beneficial responses. The iterative \
process of refining prompts in prompt engineering not only augments the \
interaction with ChatGPT but also furthers the overarching objective of \
making AI more accessible and in tune with human requirements. Furthermore, \
it furnishes invaluable insights into ChatGPT's behavior, thereby aiding \
the continuous effort to enhance and fine-tune AI systems developed by OpenAI.
"""prompt_2 = f"""
Your task is to perform the following actions:
1 - Summarize the following text delimited by
<> with 1 sentence.
2 - Translate the summary into German.
3 - List each name in the German summary.
4 - Output a json object that contains the
following keys: german_summary, num_names.
Use the following format:
Text: <text to summarize>
Summary: <summary>
Translation: <summary translation>
Names: <list of names in German summary>
Output JSON: <json with summary and num_names>
Text: <{text}>
"""
response = get_completion(prompt_2)
print("\nCompletion for prompt 2:")
print(response)Output
Completion for prompt 2: Summary: Prompt engineering is crucial for maximizing the potential of language models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT by improving the clarity and precision of responses, making AI more accessible and aligned with human needs, and providing valuable insights for enhancing and fine-tuning AI systems.
Translation: Die Gestaltung von Anweisungen ist entscheidend, um das Potenzial von Sprachmodellen wie OpenAI’s ChatGPT optimal zu nutzen, indem die Klarheit und Präzision der Antworten verbessert wird, was die Zugänglichkeit von KI erhöht und auf die Bedürfnisse der Menschen abstimmt, sowie wertvolle Einblicke für die Verbesserung und Feinabstimmung von KI-Systemen liefert.
Names: ChatGPT, OpenAI
Output JSON: { “german_summary”: “Die Gestaltung von Anweisungen ist entscheidend, um das Potenzial von Sprachmodellen wie OpenAI’s ChatGPT optimal zu nutzen, indem die Klarheit und Präzision der Antworten verbessert wird, was die Zugänglichkeit von KI erhöht und auf die Bedürfnisse der Menschen abstimmt, sowie wertvolle Einblicke für die Verbesserung und Feinabstimmung von KI-Systemen liefert.”, “num_names”: 2 }
Work on own solution
- Instruct the model to work out its own solution before rushing to a conclusion
prompt = f"""
Your task is to determine if the student's solution \
is correct or not.
To solve the problem do the following:
- First, work out your own solution to the problem.
- Then compare your solution to the student's solution \
and evaluate if the student's solution is correct or not.
Don't decide if the student's solution is correct until
you have done the problem yourself.
Use the following format:
Question:
'''
question here
'''
Student's solution:
'''
student's solution here
'''
Actual solution:
'''
steps to work out the solution and your solution here
'''
Is the student's solution the same as actual solution \
just calculated:
'''
yes or no
'''
Student grade:
'''
correct or incorrect
'''
Question:
'''
A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total.
The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball.
How much does the ball cost?
'''
Student's solution:
'''
1. The bat costs $1.00
2. Therefore, the ball costs $0.10
'''
Actual solution:
"""
response = get_completion(prompt)
print(response)Output
Let’s assume the cost of the ball is x dollars.
According to the problem, the bat costs $1.00 more than the ball, so the cost of the bat is x + $1.00. The total cost of the bat and the ball is $1.10, so we can write the equation:
x + (x + $1.00) = $1.10
Simplifying the equation, we get:
2x + $1.00 = $1.10
Subtracting $1.00 from both sides, we get:
2x = $0.10
Dividing both sides by 2, we get:
x = $0.05
Therefore, the ball costs $0.05. ’’’
Is the student’s solution the same as actual solution just calculated:
’’’
No
’’’
Student grade:
’’’
Incorrect
’’’
Model Limitations: Hallucinations
The generation of factually incorrect or nonsensical information that wasn’t present in the training data.
Causes
Overgeneralization: LLMs might overgeneralize from the patterns they have learned in the training data.
Lack of Source of Truth: Without a reliable source of truth during generation, LLMs can drift from accurate information.
Insufficient Context: Sometimes, the context provided to the model may not be sufficient for accurate generation.
Mitigation Strategies
Data Augmentation: Including a diverse range of data can help in reducing hallucinations.
External Knowledge Bases: Linking LLMs to external knowledge bases can provide a source of truth to verify generated information.
User Feedback: Incorporating user feedback can also help in identifying and reducing hallucinations.
Example
- Boie is a real company, the product name is not real.
- Output: The AeroGlide UltraSlim Smart Toothbrush by Boie is a technologically advanced toothbrush designed to provide a superior brushing experience. Boie is a company known for its innovative oral care products, and the AeroGlide UltraSlim Smart Toothbrush is no exception. One of the standout features of this toothbrush is its ultra-slim design. The brush head is only 2mm thick, making it much thinner than traditional toothbrushes. This slim profile allows for better access to hard-to-reach areas of the mouth, ensuring a thorough and effective clean. The AeroGlide UltraSlim Smart Toothbrush also incorporates smart technology. It connects to a mobile app via Bluetooth, allowing users to track their brushing habits and receive personalized recommendations for improving their oral hygiene routine…
Acknowledgments
This tutorial is mainly based on an excellent course provided by Isa Fulford from OpenAI and Andrew Ng from DeepLearningAI as well as OpenAI’s GPT best practices
What’s next?
Congratulations! You have completed this tutorial 👍
Jan Kirenz