Semantic Kernel
Introduction
Semantic Kernel
Semantic Kernel is an open-source SDK that lets you easily combine AI services like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Hugging Face with programming languages like Python.
By doing so, you can create AI apps that combine the best of both worlds.
Copilot from Microsoft
Satya Nadella at Microsoft Build 2023 about Copilot
Microsoft Copilot
Semantic Kernel is at the center of the copilot stack
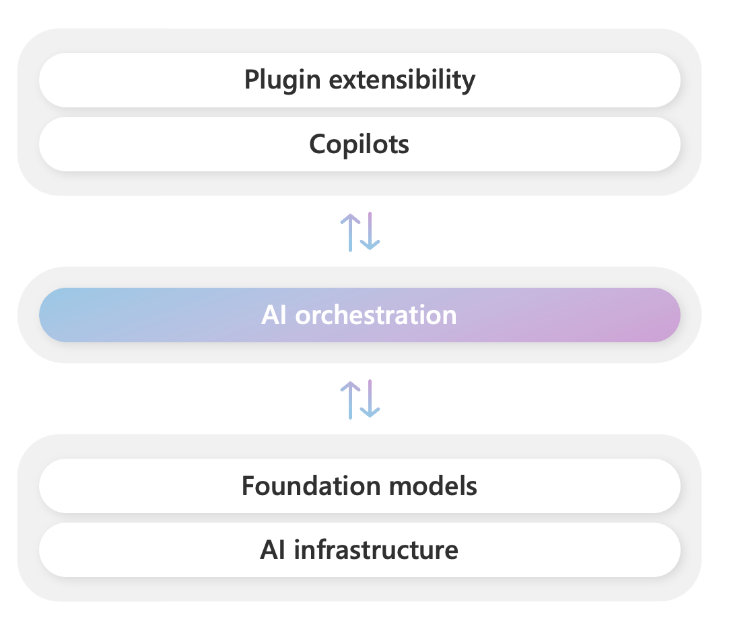
To help developers build their own Copilot experiences on top of AI plugins, Microsoft has released Semantic Kernel, a lightweight open-source SDK that allows you to orchestrate AI plugins.
With Semantic Kernel, you can leverage the same AI orchestration patterns that power Microsoft 365 Copilot and Bing in your own apps, while still leveraging your existing development skills and investments.
Who needs Semantic Kernel?
Orchestration overview
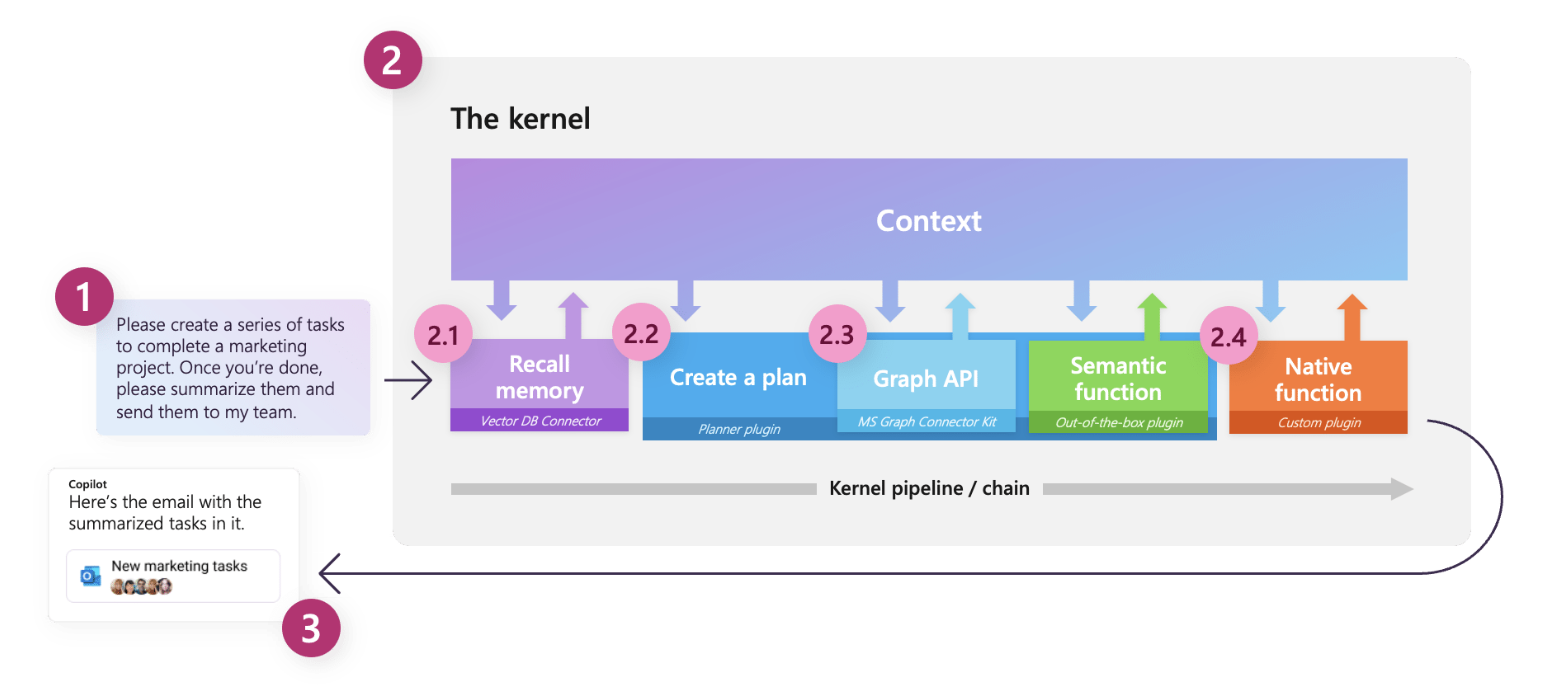
Orchestration explained
| Step | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ask | It starts with a goal being sent to Semantic Kernel by either a user or developer. |
| 2 | Kernel | The kernel orchestrates a user’s ask. To do so, the kernel runs a pipeline / chain that is defined by a developer. While the chain is run, a common context is provided by the kernel so data can be shared between functions. |
| 2.1 | Memories | With a specialized plugin, a developer can recall and store context in vector databases. This allows developers to simulate memory within their AI apps. |
| 2.2 | Planner | Developers can ask Semantic Kernel to auto create chains to address novel needs for a user. Planner achieves this by mixing-and-matching plugins that have already been loaded into the kernel to create additional steps. This is similar to how ChatGPT, Bing, and Microsoft 365 Copilot combines plugins together in their experiences. |
| 2.3 | Connectors | To get additional data or to perform autonomous actions, you can use out-of-the-box plugins like the Microsoft Graph Connector kit or create a custom connector to provide data to your own services. |
| 2.4 | Custom plugins | As a developer, you can create custom plugins that run inside of Semantic Kernel. These plugins can consist of either LLM prompts (semantic functions) or native C# or Python code (native function). This allows you to add new AI capabilities and integrate your existing apps and services into Semantic Kernel. |
| 3 | Response | Once the kernel is done, you can send the response back to the user to let them know the process is complete. |
Create Kernels
Setup
OpenAI Kernel
AzureOpenAI (optional)
HuggingFace Kernel
What’s next?
Congratulations! You have completed this tutorial 👍
Next, you may want to go back to the lab’s website
Jan Kirenz